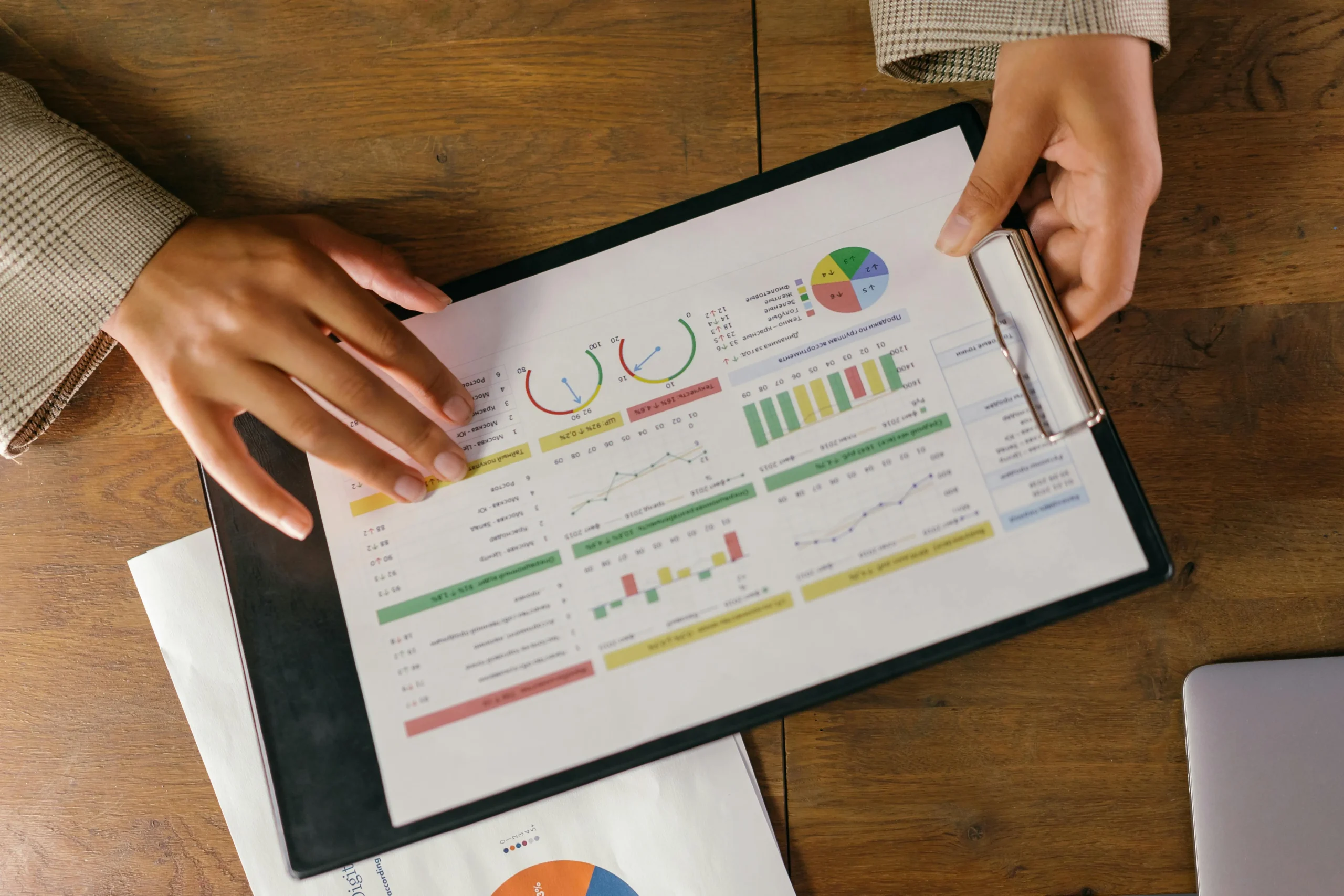
In today’s data-driven world, businesses are inundated with information. From customer profiles to product catalogs, employee records to vendor lists, data forms the backbone of decision-making and operations. However, managing this data effectively remains a significant challenge. This is where Master Data Management (MDM) comes in, offering a structured approach to managing critical business information. This guide provides an introduction to MDM, its importance, and how businesses can implement it effectively.
What is Master Data Management (MDM)?
Master Data Management is a comprehensive method used to define and manage an organization’s critical data. It ensures consistency, accuracy, and accountability across the enterprise. Master data typically includes core information about customers, products, employees, suppliers, and locations. Unlike transactional data, which changes frequently, master data serves as a stable and trusted reference point for business operations.
MDM creates a single source of truth by integrating data from multiple systems and standardizing it. This process eliminates duplicates, resolves inconsistencies, and enhances data quality.
Why is MDM Important?
The importance of MDM cannot be overstated. Here are some key benefits:
- Data Accuracy and Consistency: MDM eliminates redundant and conflicting data, ensuring that all stakeholders have access to accurate and consistent information.
- Improved Decision-Making: Reliable data allows businesses to make informed decisions, whether it’s launching a new product or entering a new market.
- Regulatory Compliance: MDM simplifies compliance with data privacy and protection regulations like GDPR, POPIA and CCPA.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Accurate customer data enables personalized interactions, leading to improved satisfaction and loyalty.
- Cost Savings: By reducing errors and inefficiencies, MDM minimizes operational costs.
Components of MDM
Effective Master Data Management comprises several components
- Data Governance: Establishing policies and procedures to manage data throughout its lifecycle.
- Data Integration: Combining data from multiple sources into a unified format.
- Data Quality Management: Ensuring data is accurate, complete, and reliable.
- Data Stewardship: Assigning responsibility to individuals or teams for maintaining data integrity.
- MDM Tools: Utilizing software solutions to automate and manage MDM processes.
Steps to Implement MDM
Implementing Master Data Management involves several key steps
- Define Objectives: Clearly outline the goals you want to achieve with MDM, such as improving customer data accuracy or streamlining supply chain operations.
- Assess Current Data: Conduct a thorough audit of your existing data to identify gaps, inconsistencies, and redundancies.
- Develop a Governance Framework: Create policies and assign roles for data governance.
- Choose the Right Tools: Invest in MDM software that aligns with your business needs. Popular tools include Informatica, Talend, and IBM InfoSphere.
- Integrate Data Sources: Consolidate data from different systems into a central repository.
- Monitor and Maintain: Continuously monitor data quality and update governance practices to adapt to evolving business requirements.
Common Challenges in MDM
While MDM offers numerous benefits, implementing it is not without challenges. Here are some common obstacles:
- Resistance to Change: Employees may be hesitant to adopt new processes and tools.
- Data Silos: Integrating data from disparate systems can be complex.
- High Initial Costs: MDM implementation requires investment in tools, training, and personnel.
- Ongoing Maintenance: Keeping data accurate and up-to-date requires continuous effort.
The Future of MDM
The future of Master Data Management is intertwined with advancements in technology. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are set to play pivotal roles in automating data quality checks, detecting anomalies, and predicting trends. Additionally, cloud-based MDM solutions are becoming increasingly popular due to their scalability and cost-effectiveness.
Organizations that embrace these innovations will be better equipped to manage their data efficiently and gain a competitive edge.
Conclusion
Master Data Management is no longer a luxury but a necessity for businesses aiming to thrive in a data-driven economy. By ensuring accurate, consistent, and reliable data, MDM enhances decision-making, improves customer experiences, and drives operational efficiency. For organizations looking to implement MDM, the key lies in adopting the right tools, fostering a culture of data governance, and staying adaptable to technological advancements.